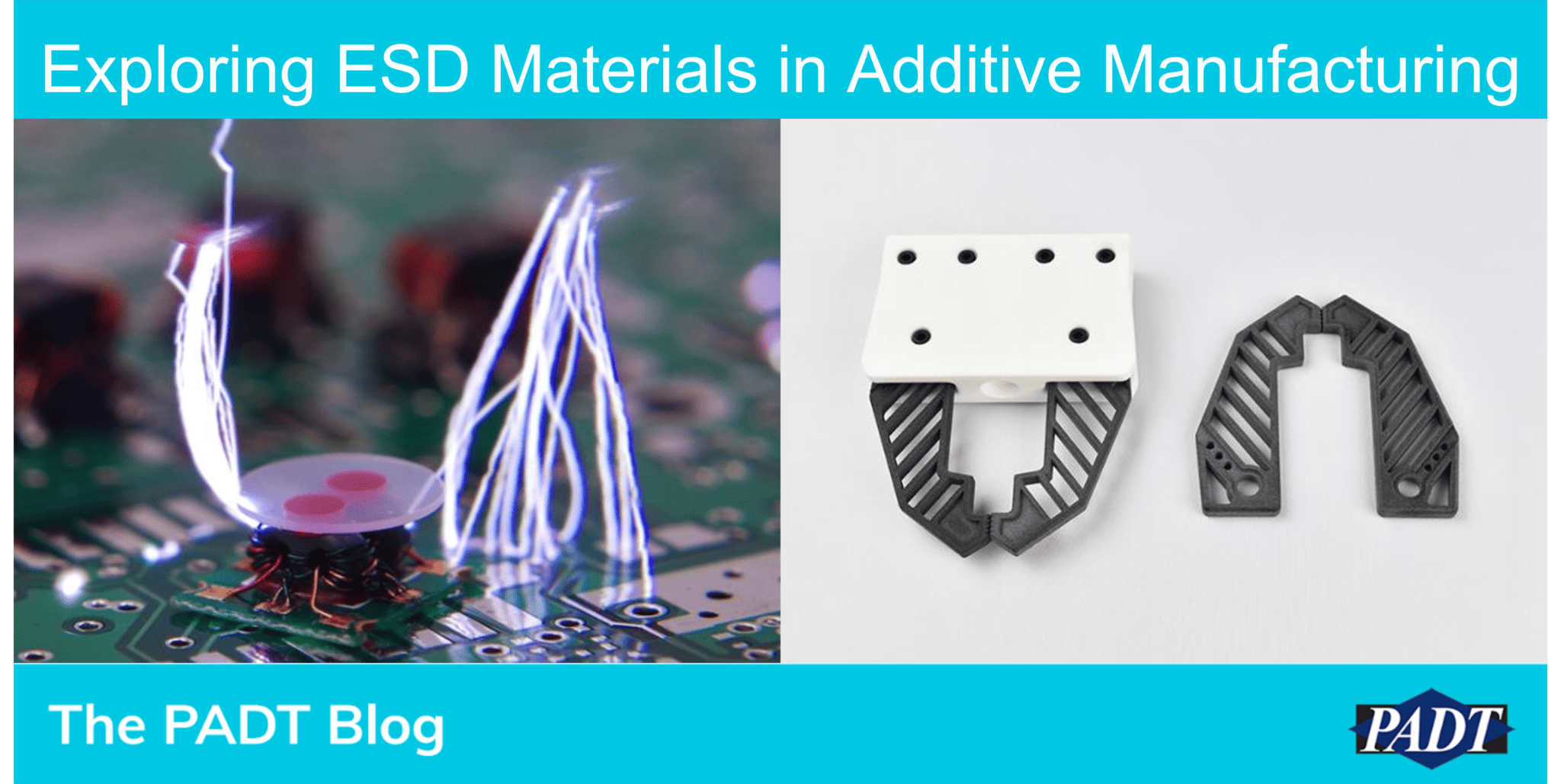
When it comes to additive manufacturing, Electrostatic Discharge (ESD) safety is super important. You don’t want to fry electronic components or damage sensitive materials, right? Unfortunately, ESD can be a real danger, but with the right precautions and using the right materials, we can prevent those risks. In this blog post, we will explain ESD, learn how to prevent it, understand the properties of ESD materials, and see how they’re used in different AM processes.
But first, if you have not read our previous blog post “3D Printing Polymer Parts with Electrostatic Dissipative (ESD) Properties”, it’s a must! It will give you great information on combining ESD behavior with 3D printing, setting up parts with ESD-enhanced filament, and ESD applications for 3D printing.
Dangers & Prevention of ESD:
Electrostatic Discharge (ESD) occurs when there is a sudden flow of electricity between two objects with different electrical potentials. This discharge can cause minor inconveniences to severe hazards. For instance, in industrial settings, there is a potential for dust explosions caused by ESD. To prevent such incidents, it is crucial to have Electrostatic Discharge Protected Areas (EPA). These areas are equipped with grounding accessories, such as ESD-safe vacuums for handling metals, which help dissipate static electricity and reduce the chance of sparks or discharges. Additionally, proper packaging and housing can also serve as preventive measures, ensuring that sensitive components are shielded from ESD. By implementing these prevention methods, the risks associated with electrostatic discharge can be reduced.
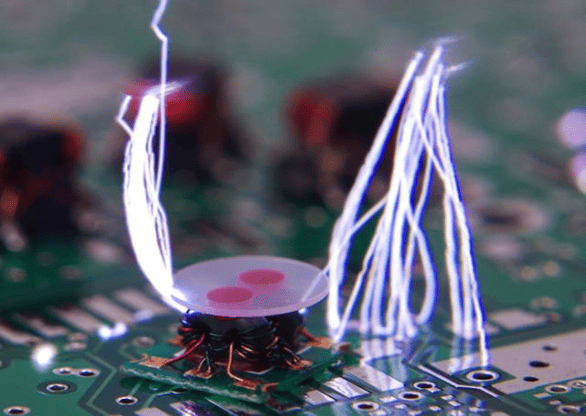
ESD Material Properties and Testing Standards:
Understanding the properties of ESD materials is crucial for selecting appropriate materials when requesting 3D-printed parts. Two commonly referenced standards for testing ESD material properties are ASTM D357 and ANSI/ESD S11.12. These standards outline test methods for measuring the DC resistance or conductance of insulating materials.
Volume resistance (Ω) and surface resistance (Ω) are important parameters measured by test equipment. However, it’s important to note that these values are:
- Not material properties
- Can be compared if using the same standard
To have meaningful comparisons, volume resistance can be converted to volume resistivity (Ω-cm) and surface resistance to surface resistivity (Ω/sq). Conductance/conductivity can be calculated by taking the inverse of resistance/resistivity.
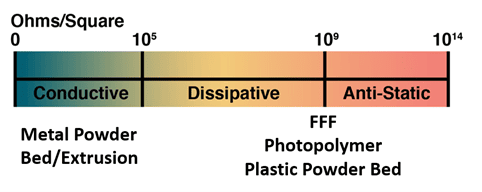
ESD in Plastic AM
In the image below you can see where different AM technologies fall on the scale. Metals are highly conductive because of their atomic structure whereas plastics have tightly bound electrons, resulting in low conductivity. However, plastics can be engineered or treated to minimize static electricity. By modifying their formulation or applying anti-static additives, plastics can gain anti-static properties. Knowing this will help make choosing the right material for your 3D printing projects easier!
Common FFF ESD Safe Materials:
Finding intrinsically ESD-safe materials for additive manufacturing is rare. However, some materials have been developed specifically to exhibit ESD properties. One example is Pomalux SD-A, a noncarbon alloy copolymer that possesses inherent ESD qualities.
Alternatively, other insulating plastics use fillers to enhance their ESD properties such as:
- Carbon black
- Graphene
- Carbon fiber
- Carbon nanotubes
- Stainless Steel
Filaments like Essentium Z-series filament utilize these fillers, making them suitable for ESD-sensitive applications in 3D printing.
Other ESD Safe AM Materials and Applications:
Beyond plastics, other ESD-safe AM materials include:
- Photopolymers, including rigid and elastomer resins for SLA/DLP/LCD processes, can be formulated with additives like carbon nanotubes (CNT) to provide ESD-safe characteristics. Companies like Tethon 3D offer C-Lite (beta) resins, incorporating CNT additives for ESD protection.
- Polymer Powder Bed, specifically Ultrasint® PA11 ESD and SAF PA11
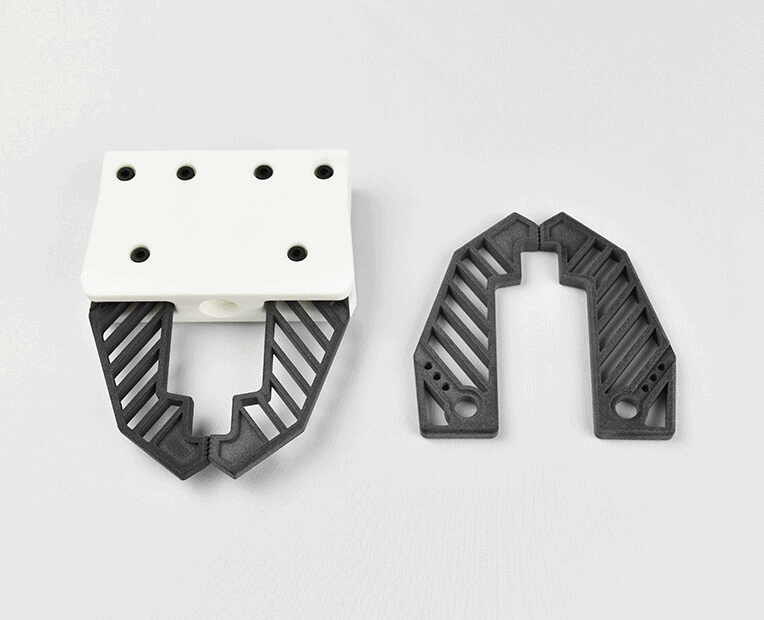

Applications of ESD materials in AM:
- Jigs/Fixtures: Nylon-ESD
- Electronics Housing: ABS/PLA/PETG/PCTG ESD
- Space Flight: PEKK(Antero) ESD
As you have read, ESD can pose a major threat to you, your electronics, parts, etc. If you need ESD-safe materials and are still unsure of where to start, please submit your quote here or email us at 3dprint@padtinc.com and one of our engineers can help you with your project(s)!
Follow us on Instagram for more 3D Printing and 3D Scanning content!